The project operates in an environment that is surrounded by numerous uncertainties. There is a lot of uncertainty, including project financing, resource availability, and potential technical issues. And these uncertainties create project risks. But what is Risk Management? What are the steps or Processes of Risk Management?
I’ll help you answer all these questions in this post.
What is Risk Management?
There is a Manager for every project. However, the manager’s job is not only to measure the risk but also to devise ways to reduce and control the risk. And this work will be done through risk management. Generally, risk management refers to the process by which potential risks are identified and analyzed and precautionary measures are taken to address the risks. Different authors have defined risk management in different ways. The following are some notable definitions:
According to J.K. Pinto, “Risk Management is defined as the art and science of identifying, analyzing and responding to risk factors throughout the life of a project and in the best interest of its objectives.”
According to Business Dictionary, “Risk Management is the identification, analysis, assessment, control and avoidance, minimization or elimination of unacceptable risks.”
According to the Economic Times, “Risk Management refers to the practice of identifying potential risks in advance, analyzing them, and taking precautionary steps to reduce or curb the risk.”
According to the Institute of Risk Management, “Risk Management is the systematic process of understanding, evaluating and addressing these risks to maximize the chances of objectives being achieved and ensuring organizations, individuals and communities are sustainable.”
According to Investopedia, “Risk Management is the process of identification, analysis and either acceptance or mitigation of uncertainty in investment decision making.”
In light of the above definitions, risk management is the process of identifying unwanted risks, analyzing, evaluating, and taking precautionary measures to reduce, control, or avoid risks.
Steps/Process of Risk Management
Risk management is a process where some interrelated steps are followed. The risk management process is described below:
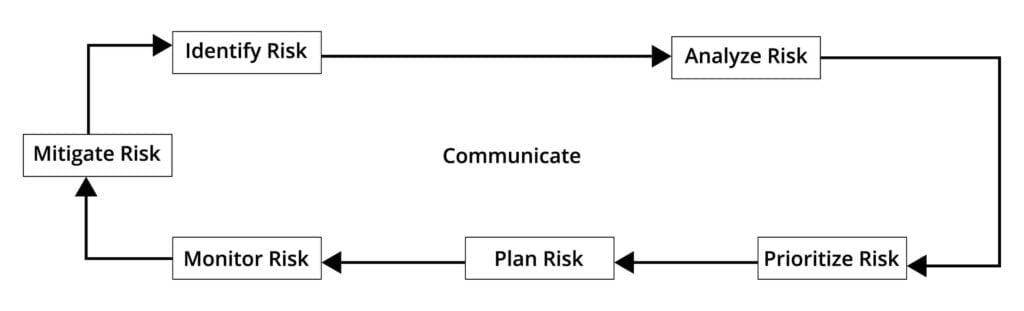
- Identify Risk: The first step in the risk management process is to identify the risks associated with the project. Project risks can be related to production costs, financing, schedules, contracts, relationships, diplomacy, etc. that affect the project in many ways. In addition to identifying risks, risk factors are identified and who will be responsible for risk management.
- Analyses Risk: The next step after risk identification and assessment is to analyze the risk. Identified risk is converted into decision making information through risk analysis. As a result, the probability of each risk is considered and judged and the decision is made considering the severity of the risk. There are two main tasks involved in risk analysis. Namely – (i) Assessing the probability of loss (ii) Assessing the effect of loss.
- Assess The Probability of a Loss Occurring: There are some risks that often occur. Again there are some risks that rarely occur. So a scale needs to be created to determine the probability of damage. For example, on a percentage scale, the probability of loss is 10%.
According to the retention, the chances of non-loss are very high, the damage can be done and the damage will be repeated. These can be expressed again in numbers. For example, the probability of non-loss is very high = 10%, the probability of loss is = 25%, and the loss will be recurrent = 50%, etc. - Assess The Impact of the Loss: The outcome of the risk is to be described and the impact of the risk on the project is to be calculated. For example, if there is a delay of 2 weeks to deliver the goods, the amount of loss is 10,000 rupees. Alternatively the effect of loss is 1 = slight, 2 = marginal, 3 = critical, or 4 = catastrophe etc.
- Assess The Probability of a Loss Occurring: There are some risks that often occur. Again there are some risks that rarely occur. So a scale needs to be created to determine the probability of damage. For example, on a percentage scale, the probability of loss is 10%.
- Prioritize Risk: Not all risks are equally important. There are some risks that have very low impact or the risk is very low or both. Again there are some risks that have a very high impact or the risk is very high or both. Therefore, the risk manager prepares the list by selecting the risk on the basis of priority. The risks that are most likely to occur, the risks that are most affected are displayed at the top of the table. And the risks that are less likely to occur, the risks that are less effective are displayed at the bottom of the table. In this case, banking is done by determining the amount of risk. The formula for determining the amount of risk is as follows:
Risk Exposure (RE) = p * C
Where,
P = Probability of Occurrence for risk and
C = Impact of the loss to the product should the risk occur.
Example: If the probability of a risk is 10 percent and the impact of the risk is TK. 10,000. The Risk Exposure = (0.10)(TK.10,000) = Tk.1,000.
If the risk exposure of each risk is determined then the risk priority is determined based on the numerical ranking of the risk exposure.
After selecting the risk priority, the risk analyst will determine the cut off line. And the risks have to be taken very seriously. - Plan Risk: The risk manager will plan the risk based on the importance and priority of the risk so that precautionary measures can be taken to deal with the risk. The following are some of the classifications of risk planning functions:
- Information Buying: The risk can be reduced by gathering more information through research. In order to minimize the risks posed by such technological changes, new technology infrastructure can be developed and the organization’s employees can be trained on new technologies.
- Contingency Plans: A potential risk plan is a plan that describes what to do if a risk occurs.
- Reduction Risk: Risk analysts will search and determine the risk reduction approach.
- Risk Acceptance: Many times the organization cannot avoid the risk even if it wants to. Therefore, the organization consciously takes measures to deal with the risk by knowing the consequences of the risk and the consequences of the possible loss and accepting the risk.
- Mitigate Risk: The risk manager will formulate some strategies in line with the risk plan to minimize the risk potential and the impact of the risk. Risk mitigation creates a situation where the risk is eliminated or controlled. Risk mitigation strategies are as follows:
- Risk Avoidance: Risk managers can avoid risks in some cases. Do not develop products that pose such risks.
- Risk Protection: An organization can provide risk protection through insurance. However, in the case of risk mitigation, the cost-benefit analysis needs to be done to see if the risk mitigation benefit outweighs the risk mitigation cost. In this case, risk-leverage can be determined and cost-benefit analysis can be done. The formula for determining risk leverage is as follows:
Risk Leverage (RL) = (Risk Exposure before Reduction – Risk Exposure after Reduction) / Cost of Risk Reduction
If the value of Risk Leverage is ℼ ≤ 1 then the benefit of risk aversion is less than the cost of risk aversion. If the value of RL is slightly higher than 1 then the benefit is more than the cost but this raises many questions because the basis of all these diagnoses is probable data but not actual data. That is why the risk is multiplied by the discount rate and the discounted leverage value is determined to get the right result. If the discounted leverage value is not adequate and acceptable, the risk manager will look for less costly or more effective risk avoidance strategies.
- Monitor Risk: After identifying the risk, analyzing, prioritizing, planning the risk, determining the steps to be taken to mitigate the risk, it is necessary to examine the existing risk of the project and the effectiveness of the risk mitigation/control strategy. The risk manager will regularly monitor the risk and take corrective action if necessary. Risk should be assessed at regular intervals to see if any new conditions have arisen which have increased the likelihood or impact of the risk. In this case, some new risks may be added and some risks may be eliminated. So we need to redefine the risk priority to see which risks are above the cut off line and which risks are below. Action needs to be taken for all the risks that are above the risk line and action is not required for all the risks that are below the risk line. However, a successful risk manager will take precautionary measures.
- Communicate: Maintain ongoing and effective communication about project risk with managers, development teams, marketing, and buyer representatives for successful risk management. Communication is said to be the cornerstone of effective risk management as all information is communicated through communication.
Through the above process, the risk manager performs the functions of risk management.

